| Knee injuries main |
|
|
What is the Rotator Cuff Injury?The Rotator Cuff is a name given 4 muscles that surround the shoulder. They stabilize and mobilize the shoulder and arm. A rotator cuff injury can occur in 1 or more of these muscles in the shoulder. These 4 major muscles are:Subscapularis Infraspinatus Supraspinatus (must commonly damaged muscle) Teres minor Feeling for tender areas can help determine the muscles that are affected. The shoulder can also be tested for deformity or muscle weakness to reveal which muscles have been injured. Learn about the muscles and tests below. You usually need another person for the test because they involve force being applied to an action. However they can be done against a wall or solid stationary object. Subscapularis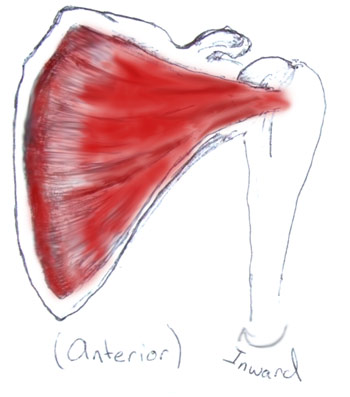 The subsacpularis muscle originates from the underside of the shoulder blade and inserts at the front of the upper arm (humorous). Action It medially rotates the arm and also helps to extend the arm. The deltoid muscles elevate the arm further. Test This test involes holding the hand behind the back (like a police arrest hold except into a mild boudary) with the palm facing away from the body. Push gently on the palm away from the back while a gentle force is applied forward. If the muscle is injured pain will occur. If only mild or no force can be applied the muscle may be torn. Infraspinatus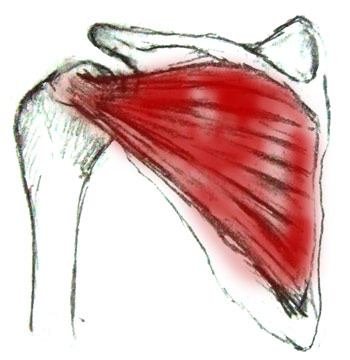 The origin of the infraspinatus is the fossa of scapula. It inserts into the back of the shoulder joint capsule (posterior aspect of greater tuberosity of humerus). Action The infraspinatus muscle laterally rotates the arm. It is the primary muscle force resposible for external rotation. It also adducts the arm and is involved in extension at the shoulder joint. Test Slightly abduct the arms and bend the elbows bent at 90 degrees. Place your hands on the outside of their arms. Encourage gentle force that opens their arms and externally rotates them. Supraspinatus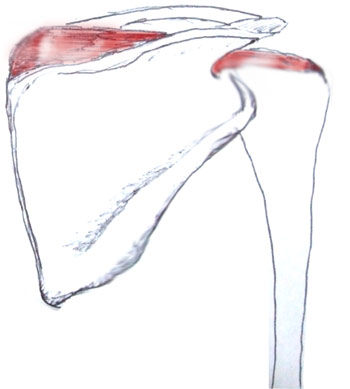 The supraspinatus muscle is the most commonly damaged rotator cuff muscle. Its origin is the supraspinatous fossa and its insertion which is the highest facet on the humerus is the greater tubercle of the humerus. Action The supraspinatus is one of the first muscles to act in adducting the arm away from the body. It is als a stabilizer in the shoulder joint in both anterior and posterior stability. Test Test the Supraspinatus on your own by simply adducting the arms away from the body. An inability to do this simple motion indicates a complete tear in the supraspinatus muscle. Move the arms into a slight horizontal abduction and 90 degrees of forward flexion where the arms are shoulder width apart. Apply resistance to upward force. Another useful test is called the drop arm test. The arms are abducted out 90 degrees which is horizintally aligned with the shoulders. They are then lower slowly and with control. Pain can indicate supraspinatus damage. Teres Minor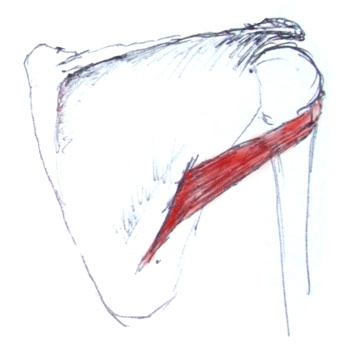 The Teres Minor origin is and its insertion is the lower shoulder joint capsule (inferior aspect greater tuberosity of the humerus) Test The test is the same as the infraspinatus muscle. Abduct the arms and bend the elbows bent at 90 degrees. Place your hands on the outside of their arms. Encourage gentle force that opens their arms and externally rotates them. |
If your a yoga teacher you may want to learn some of the tests shown under the images. Some of these tests can be done gently while someone is performing a posture. If a student complains about shoulder pain give advice on the appropriate modifications that do not endanger the joint or have a high possibility of aggravation. The more you know about the body and how it is affected by injuries the more you can help and not aggravate symptoms further. If you are a student and want to keep doing yoga but have a bad shoulder follow the advice below on modifications and tips to prevent shoulder instability and inflammation following a class.  Paschimottasana is a seated forward bend in yoga. It is a good way to stretch the hamstrings. If the anterior meniscus is damaged maintain a slight bend but if the posterior meniscus is damaged straighten the legs to relieve the pressure. Use ice packs to help with swelling and reduce pain. |
ACL injury Meniscus injury Patella Tracking |